Shockwave Therapy For Tendonitis
Posted By: Forward Wellness
Pain caused by tendon dysfunction or tendon injuries sustained during sports can be difficult to manage. This pain can impair your strength and motion, causing stress on your body. Conditions like tendonitis (the inflammation of the tendon) can make you incapable of exercising and doing things the way you would love to. As a result, the quality of your life can be affected.
Pain relief medication may be used to manage tendonitis. Though regularly using medications will help relieve your discomfort and pain, you may still experience some side effects of your injury such as decreased strength and motion.
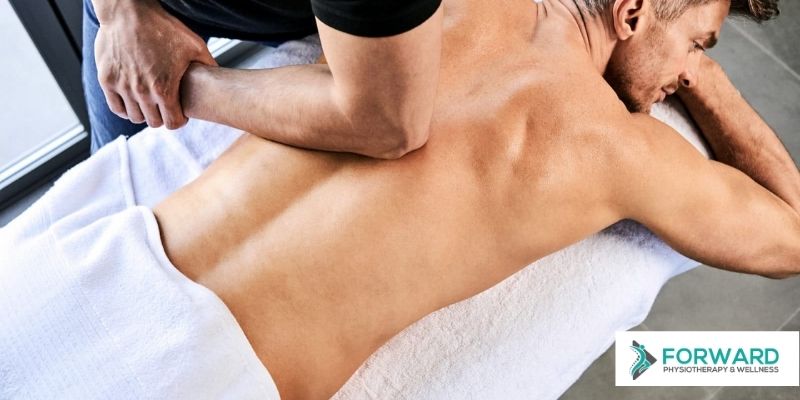
An innovative treatment option to help patients with tendon problems is shockwave therapy. Shockwave therapy can target pain in the ligaments, muscles, joints, bones, and tendons. It is a special procedure that makes use of either electromagnetic pulses or pressurized air to deliver shockwaves to the body. This shockwave helps in treating a variety of disorders and is shown to be an effective option for tendon injuries.
This treatment is non-invasive, and it can be delivered as an outpatient treatment. The shockwave treatment can lead to a significant decrease in pain symptoms.
What is shockwave therapy?
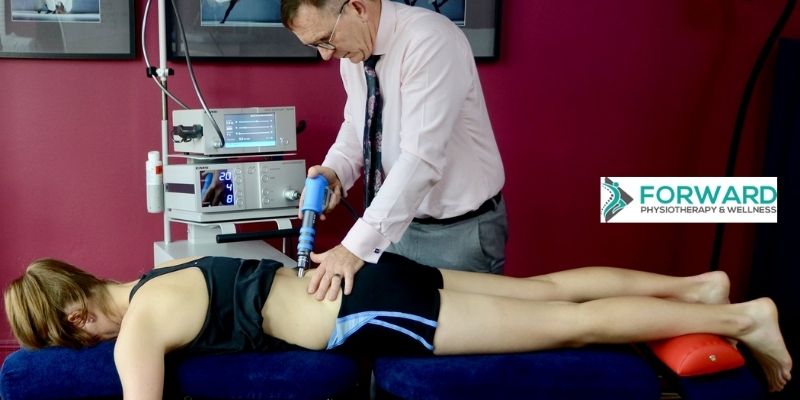
Shockwave therapy is known also as Radial Shockwave Therapy (RSWT) or Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT). The therapy was initially developed to non-invasively help treat kidney stones; however, it recently started being used in the treatment of many musculoskeletal conditions like painful muscles, joints, and tendons.
Shockwave therapy typically has no major side effects. It is highly recommended for use in treating musculoskeletal conditions.
Conditions where shockwave therapy is used
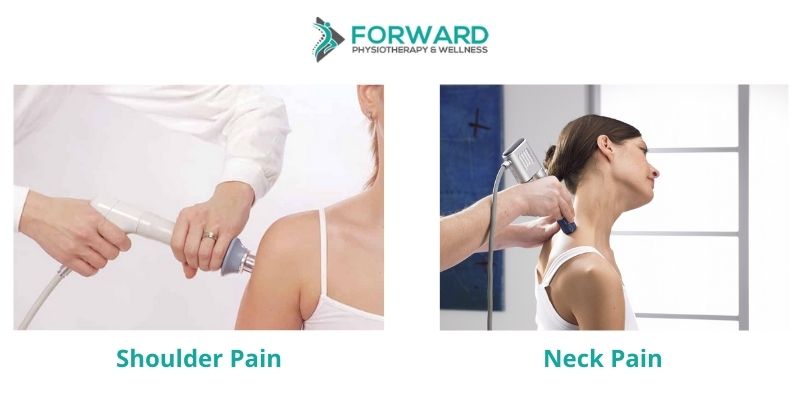
The use of shockwave therapy is beneficial to patients with bone and joint conditions, and painful soft tissues which include the tendons, ligaments, and muscles. It is often combined with physiotherapy or chiropractic therapy as an adjunct to a treatment plan made by your health professional.
Shockwave therapy is commonly used to treat the following conditions:
- Chronic back and neck pain
- Hip joint pain
- Tendon pain cause by repetitive overuse
- Running injuries (Knee pain, Heel pain)
- Shoulder pain (Rotator Cuff)
- Shin splits
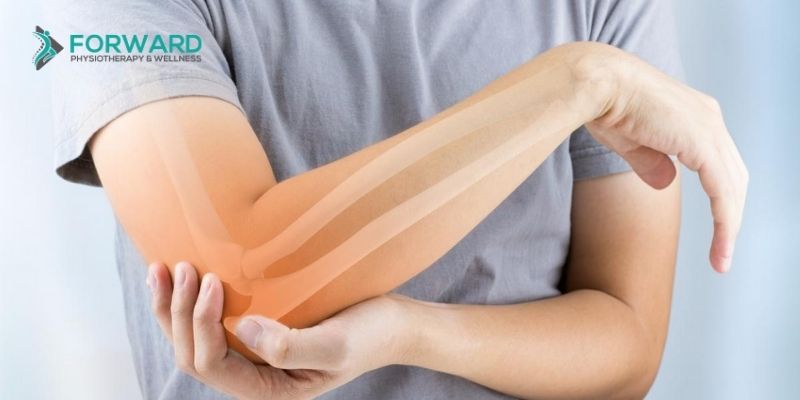
- Tendonitis (Elbow, Knee, Rotator Cuff)
How shockwave therapy works
Shockwave therapy is a targeted type of therapy that can either be in the form of low-energy or high-energy. It can be used to treat the affected or injured areas. Tendonitis can be treated with both forms of shockwave therapy.
The low-energy form of the shockwave is mild or not painful. It involves a series of treatments that can be done three or more times. High-energy shockwave therapy, on the other hand, can be more uncomfortable. Unlike low-energy shockwave therapy, treatment with high-energy therapy may only need a single session.
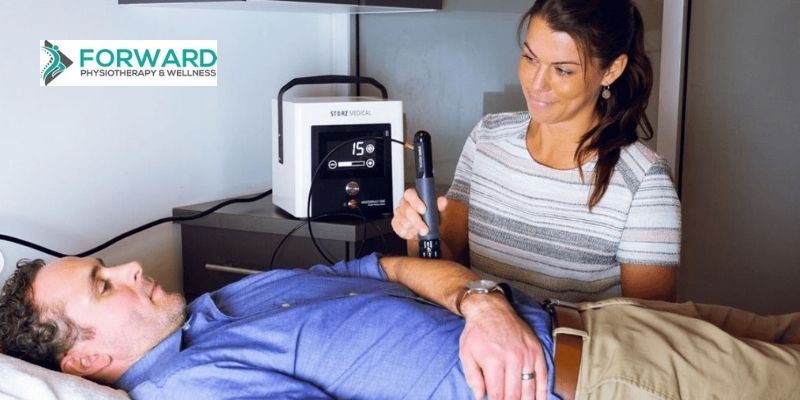
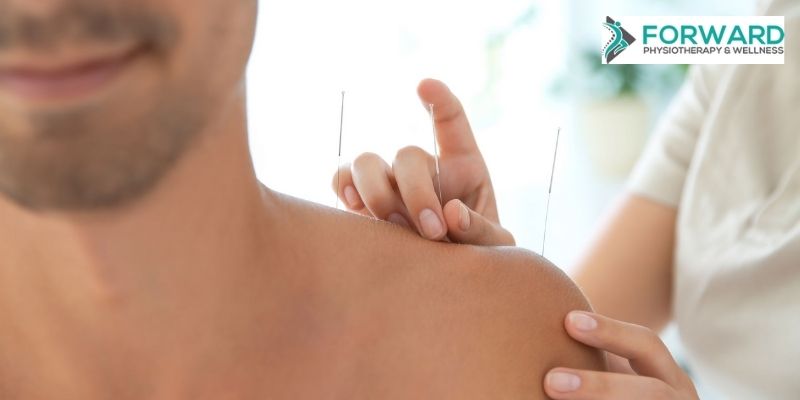
The shockwave therapy is administered over the tendons which are affected. Rather than using electrical waves for pain relief, it uses acoustic or sound waves. The behavior and shape of the sound waves are radial-like. They penetrate the skin easily and radiate as a shockwave through the affected tendon.
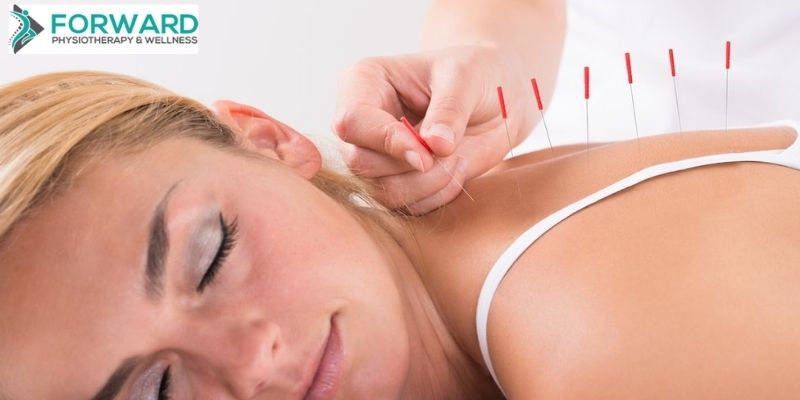
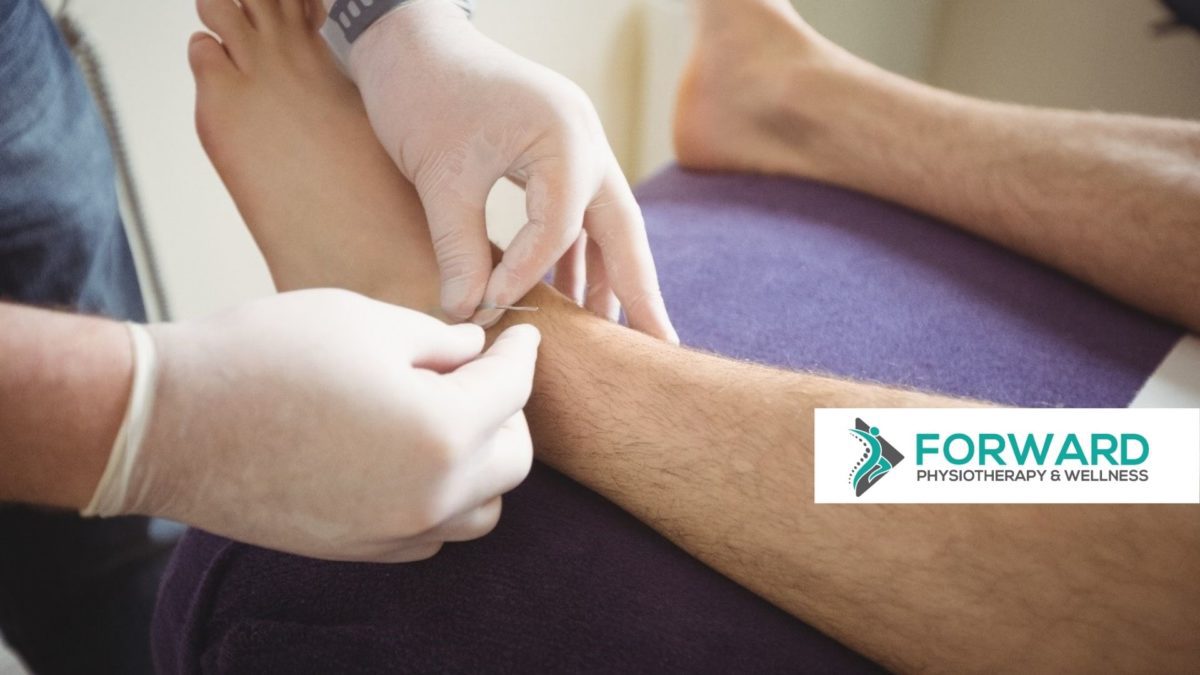
When performing shockwave therapy, the therapist will make use of a handheld device that turns compressed air into sound waves. Slight pressure will be applied as the device is moved over the tendon that needs treatment. Beforehand, ultrasound gel is applied to the skin. This will help transmit the shockwave through the skin and improve glide of the device.
The sound wave causes the stimulation of blood flow to the tendons. This may result in an "inflammatory healing response" around the tendons. This response facilities the natural healing process in the body for a few days after treatment. This healing process encourages the regeneration and repair of the cells. The pain reduces as the soft tissues around the tendons begin to repair.
Who should not take shockwave therapy?
Before administering your treatment using shockwave, the therapist will first assess its suitability for you. Although it is a safe and effective treatment, it is not recommended in some circumstances.
Some examples of these circumstances are:
- Being pregnant
- Having a nerve disorder
- Having any kind of cancer
- Having blood clotting disorder
- Having infections around the tendons
- Having received steroid injection in the same area recently
Benefits of shockwave therapy
The benefits of shockwave therapy are many. Its success rate makes it an attractive option for tendonitis. Some of the benefits of this treatment are:
Non-surgical and non-invasive: Shockwave therapy is a non-surgical and non-invasive treatment. There is no need to invade the body tissue when having treatment. Treatment is simply carried out through the body's soft tissues. This is done by directing acoustic or sound waves to the tendons.
Stimulates the flow of blood: A reduction in the flow of blood may contribute to the pain of tendonitis. Focusing acoustic energy on the tendons can stimulate a greater flow of blood. This helps to generally enhance the natural regenerative abilities of the body.
No downtime: No downtime is associated with shockwave therapy because it is a non-surgical and non-invasive treatment. Patients have few restrictions after treatment, and they are allowed to carry on with their daily activities.
Dissolves the build-up of calcium: The build-up of calcium called osteophytes around the joints and tendons can limit the range and mobility of motion and increase pain. There is some evidence that shockwave therapy can help dissolve any build-up of calcium in these areas of the body.
Reverses chronic inflammation: Chronic inflammation can contribute to chronic pain. Abnormalities and injuries in the body are generally the cause of inflammation. Inflammation is a necessary part of healing but prolonged inflammation can prolong pain. Shockwave therapy may reduce inflammation, which allows the body to heal and recover fully.
Interrupts pain neurotransmitter: This therapy interferes with the main pain neurotransmitter of the body. It prevents it from sending messages to the brain’s nerve receptors. Since some neurotransmitters and neuropeptides are associated with chronic pain, shockwave therapy blocks these adverse and pain-causing body communications and leads to a decrease in pain levels.
Conclusion
Shockwave therapy is an excellent therapeutic modality to consider because it is a non-surgical and non-invasive treatment option for tendonitis. It is a safe, simple, and effective treatment. However, it is not recommended in certain conditions. Your physiotherapist will advise you on the best course to take when considering this treatment.