INJURIES AND CONDITIONS THAT WE TREAT
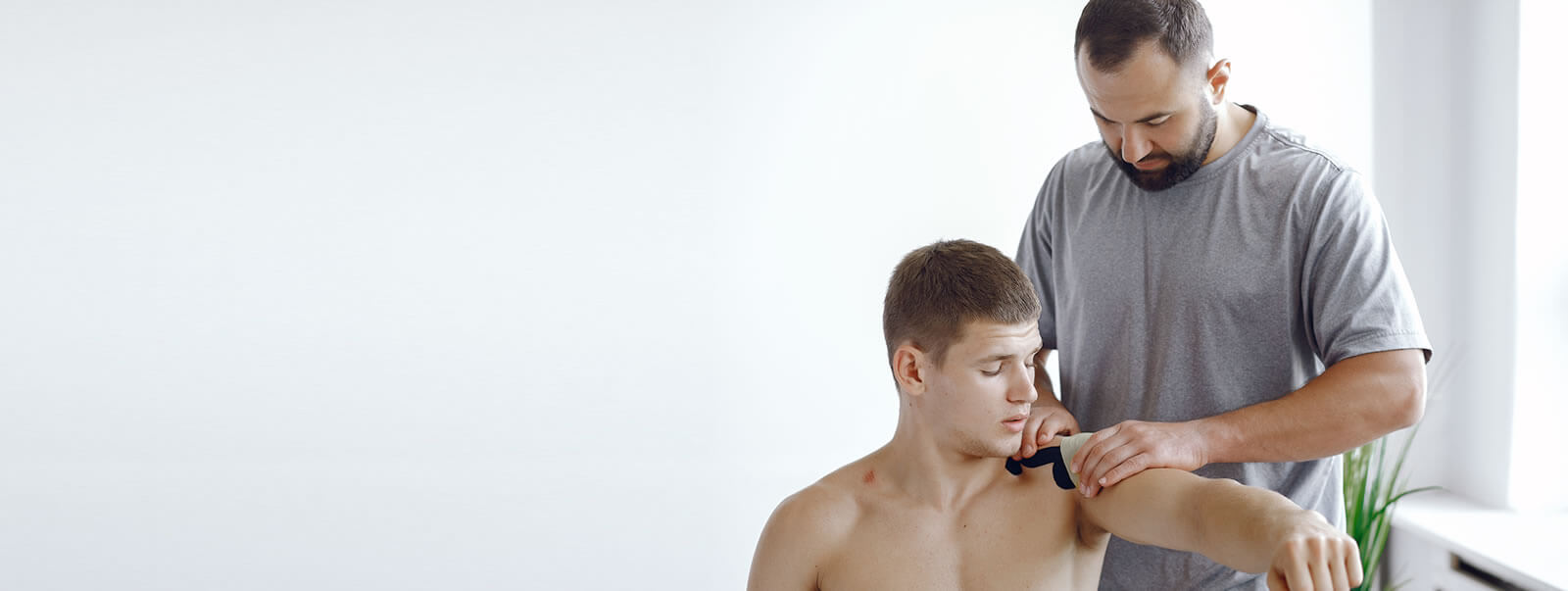
SHOULDER PAIN TREATMENTS
- Impingement is the compression and irritation of tissue as it travels through a bony space in your shoulder called the subacromial space. The tissues that travel through this space include bursa, rotator cuff tendons, biceps tendon, and ligament.It often causes pain on the front or side of your shoulder, especially when the arm is elevated. This condition may also be diagnosed according to which tissue is affected, ie. rotator cuff. Your therapist will assess your shoulder and create a treatment plan to resolve your symptoms. Learn More
- Learn More
- The AC joint is one of the 4 joints of the shoulder. It is formed by your clavicle (collar bone) and a segment of your scapula (shoulder blade) called the acromion. It is located on the top of your shoulder and when injured may lead to a bony “bump” on the top of your shoulder. Injury usually occurs in the form of trauma that causes disruption to the ligaments of the AC joint, or this joint can be susceptible to degeneration as well. Your therapist can assess your AC joint to see if it is a contributing factor to your pain and create a treatment plan to address your concerns.Learn More
- The SC joint is one of the 4 joints of the shoulder. It is formed by your clavicle (collar bone) and sternum. This joint is located on the front of your chest. There is only a small amount of movement that occurs here when the shoulder blade moves. This joint is usually fairly stable due to the strong ligaments but injury is possible following trauma or collar bone fracture. Your therapist will be able to assess this joint and create a care plan to restore your function. Learn More
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome involves an area on the front of your neck/chest/shoulder called the thoracic outlet where important structures pass through on the way to your arm such as the nerve, artery, and vein. This passage can become narrowed or restricted due to injury, inflammation, poor posture, or tight muscles. Compression of the nerve, artery, and vein can lead to symptoms such as numbness and tingling in your hand, and a “heavy” or “cold” sensation in your hand or swelling of the hand. Your therapist will do a series of tests to determine the cause of your symptoms and create a treatment plan to address your concerns. Learn More
- A bursa is a fluid filled “sac” that acts as a cushion between bone and tendon/muscle to reduce friction. In the shoulder, there are many bursae present. Bursitis is a swelling/inflammation of one of these sacs that can cause painful motion. Bursitis can occur from trauma, irritation, poor posture, impingement, overuse, degeneration in the area, or other injuries in the area that cause inflammation for example a torn rotator cuff can cause inflammation in the area and anger the bursa. Your therapist will examine your shoulder to determine if bursitis is the cause of your pain and create a treatment plan to get you on the path to recovery. Learn More
- The labrum is the cartilage that is attached to the inner surface of the shoulder joint or the shoulder “socket”. Injury can occur from trauma like a fall, repetitive overhead motion such as baseball pitchers, shoulder dislocation, or degeneration. When an injury or tear occurs in this cartilage it can produce symptoms of pain, clicking or “clunking” and a feeling of instability. Your therapist will complete a thorough shoulder assessment and create a treatment plan to get your shoulder back in shape. Learn More
- After seeking medical attention for your fracture (x-ray, casting, etc) it is important to complete physiotherapy to restore the function of your arm. After being in a cast, the arm, elbow, wrist, and hand may feel stiff and you may have lost some motion ie. not being able to reach above your head or reach behind your back. Your muscles have usually lost strength as well due to not being used while in the cast. Your therapist will create a plan to restore the function in your shoulder and arm and get you back to your favorite activities. Learn More
- Adhesive capsulitis (also known as frozen shoulder) is a condition that affects the shoulder joint capsule (the tissue that surrounds the shoulder joint). Frozen shoulder leads to a tightening and inflammation of this capsule and symptoms include pain and severe restriction of shoulder movement leading to limitations on daily activities like being able to get dressed or brush your hair or sleep. The cause of frozen shoulder is still controversial as many cases seem to be insidious (meaning no known cause). Current evidence suggests there may be risk factors that predispose you to frozen shoulder including trauma or previous shoulder injury, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or other medical conditions such as hypothyroidism, Parkinson’s, and tuberculosis. The journey of frozen shoulder is long-term with symptoms lasting months to years. Your therapist will assess your shoulder and create a long-term treatment plan to ease your discomfort and get back to daily activities. Learn More
- The biceps is the muscle on the front of your arm. The bicep has two portions or “heads” - the short head and the long head. The long head of the biceps inserts in the shoulder and the tendon can be felt on the front of the shoulder (site of pain). Tendinopathy is an inflammation and irritation of the tendon leading to pain. Cause of tendonitis involves repetitive activity, overloading, or due to inflammation from other nearby injuries such as the rotator cuff. When left untreated, chronic tendinopathy may weaken the tendon structure and lead to eventual rupture or tear. Your therapist will assess your biceps tendon and create a treatment plan to help resolve your symptoms. Learn More
- Rotator cuff tears are the leading cause of shoulder pain and shoulder disability. There are 4 muscles in your rotator cuff - supraspinatus, subscapularis, infraspinatus, and teres minor. These muscles sit on your shoulder blade and insert into the shoulder. Their main job is to stabilize the shoulder joint during movement and contribute to rotation. Rotator cuff tears can be caused by trauma, falls, degeneration, repetitive motion, or overload. There is evidence that smoking, frozen shoulder, and rotator cuff tendonitis can increase your risk of rotator cuff tears. Symptoms include pain with overhead activity, shoulder stiffness, and weakness. Your therapist will assess your shoulder to determine the health of your rotator cuff and create a treatment plan to address your pain. Learn More
- There are 4 muscles in your rotator cuff - supraspinatus, subscapularis, infraspinatus, and teres minor. These muscles sit on your shoulder blade and insert into the shoulder. Their main job is to stabilize the shoulder joint during movement and contribute to rotation.Tendinopathy is an inflammation and irritation of the tendon leading to pain. Cause of tendonitis involves repetitive activity, overloading, or due to inflammation from other nearby injuries. When left untreated, chronic tendinopathy may weaken the tendon structure and lead to eventual rupture or tear. Your therapist can assess your rotator cuff and create a treatment plan to restore the function of your shoulder.Learn More
- The shoulder joint has the highest mobility in the body, but this often comes at the cost of decreased stability. Instability is the excessive movement of the shoulder joint “ball” in the socket. The cause of instability includes injury to the ligaments or muscles that stabilize the shoulder or some individuals naturally have laxity or “looser” joints. Symptoms of instability include pain, clicking, and “apprehension” or feeling that the shoulder is going to dislocate. Instability may lead to dislocations if not addressed. Your therapist will address your shoulder and create a treatment plan to restore the joint stability.Learn More
- In a healthy shoulder, there are many constraints that keep the shoulder in place such as muscles, ligaments, and the labrum. Shoulder dislocation can occur during a trauma like a fall or you may be at risk of dislocation if you have some shoulder instability following previous ligament injuries. Therapy is important in these cases as one dislocation can lead to more future dislocations if the shoulder remains unstable. Your therapist will assess your shoulder and create a treatment plan to restore stability.Learn More
- The shoulder is a complex area comprising 4 joints as well as many ligaments and muscles. The shoulder joint has the highest mobility in the body! Shoulder pain can have many causes including tendonitis, tears, bursitis, fracture, and more. Occasionally shoulder/arm pain may even be caused by your neck or posture. Your shoulder is involved in many important functional tasks such as lifting, reaching, and daily tasks. If you are having shoulder pain, your therapist can narrow down the cause and create a treatment plan to get you on the path to healing. Learn More


